Cold Sore vs Canker Sore: Symptoms, Causes & Treatments Compared
Introduction
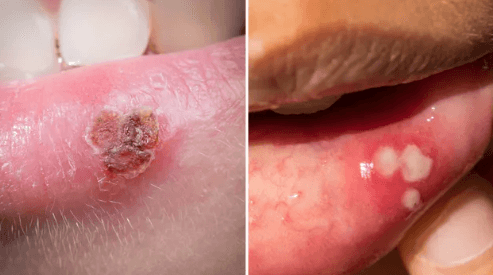
Struggling to tell a cold sore from a canker sore? Although they may seem similar, these two common mouth lesions have different causes, appearances, and treatments. Cold sores (also called fever blisters) are caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV-1) and are contagious, while canker sores (aphthous ulcers) occur inside the mouth, are non-contagious, and often develop due to triggers like stress, injury, or nutritional deficiencies.
In this article, we’ll break down their differences in detail—covering symptoms, causes, triggers, contagiousness, treatment, and prevention—so you can easily identify and manage them. Understanding the difference helps you treat symptoms faster, reduce recurrence, and avoid unnecessary worry.
1. What Are They?
- Cold Sores: Also known as fever blisters or oral herpes, cold sores are caused by the herpes simplex virus (usually HSV-1, sometimes HSV-2). They are highly contagious and often triggered by sun exposure, stress, or illness. Once infected, the virus remains dormant in the body and can reactivate at any time.
- Canker Sores: Medically called aphthous ulcers, these are common non-contagious mouth ulcers caused by immune system reactions, nutritional deficiencies, food sensitivities, or injury to the mouth lining. They can occur in people of all ages and are not linked to viral infection.
LSI Keywords: fever blisters, aphthous ulcer, mouth ulcers, herpes labialis, oral stomatitis.
2. Location & Appearance
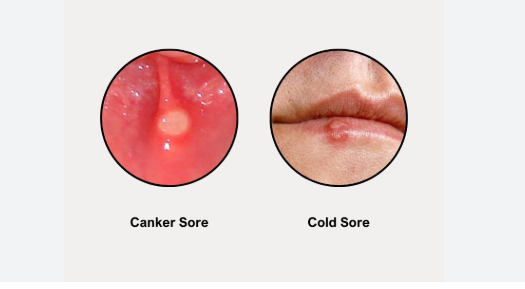
- Cold Sores: Appear as small, fluid-filled blisters that often cluster together on or around the lips, sometimes near the nose or chin. They go through stages—tingling, blistering, crusting, and healing.
- Canker Sores: Develop inside the mouth—on the tongue, inside cheeks, lips, or soft palate. They appear as round or oval ulcers with a white or yellow center and a red border.
3. Causes & Trigger
- Cold Sores: Caused by HSV-1 infection. Triggers for reactivation include stress, fatigue, illness, sunburn, hormonal changes, or a weakened immune system.
- Canker Sores: Not caused by viruses. They can be triggered by stress, mouth injury (biting your cheek, dental work), food sensitivities (spicy, acidic foods), deficiencies in iron, folate, vitamin B12, hormonal changes, or autoimmune conditions like celiac disease.
4. Symptoms & Timeline
- Cold Sores:
- Early symptoms: tingling, itching, or burning sensation around the lips.
- Within 24–48 hours, blisters form, break open, crust over, and heal in 7–14 days.
- May be accompanied by fever, sore throat, or swollen lymph nodes during initial infection.
- Early symptoms: tingling, itching, or burning sensation around the lips.
- Canker Sores:
- Early symptoms: tingling or burning in a specific spot inside the mouth.
- Ulcer appears with white or yellow center, red edges, and mild to severe pain when eating or speaking.
- Minor sores heal in 7–10 days; major or herpetiform types can last longer and may scar.
- Early symptoms: tingling or burning in a specific spot inside the mouth.
5. Contagiousness & Risk
- Cold Sores: Extremely contagious from the first tingling stage until completely healed. Spread through kissing, sharing utensils, towels, razors, or direct skin contact.
- Canker Sores: Not contagious. Cannot be transmitted from person to person.
6. Treatment & Relief
Cold Sore Treatments:
- Antiviral creams such as acyclovir, penciclovir, or docosanol applied at the first symptom can shorten healing time.
- Oral antiviral medications like valacyclovir or famciclovir are prescribed for severe or frequent outbreaks.
- Pain relief: ice, cold compresses, and over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Lip protection: use SPF lip balm to prevent sun-triggered outbreaks.
Canker Sore Treatments:
- Usually heal without treatment.
- Topical anesthetics (lidocaine, benzocaine) for pain relief.
- Antimicrobial mouth rinses to reduce bacterial load and speed healing.
- Corticosteroid ointments for severe or recurrent cases.
- Avoid spicy, acidic, or abrasive foods during healing.
7. Prevention Tips
For Cold Sores:
- Avoid direct contact (kissing, sharing items) during outbreaks.
- Use lip balm with SPF.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, or meditation.
- Maintain a strong immune system with proper diet, sleep, and hydration.
- Discuss daily antiviral therapy with a doctor if outbreaks are frequent.
For Canker Sores:
- Identify and avoid trigger foods.
- Switch to toothpaste without sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS).
- Maintain good oral hygiene without harsh brushing.
- Correct nutritional deficiencies through a balanced diet or supplements.
8. Key Differences at a Glance
| Feature | Cold Sore | Canker Sore |
| Cause | Herpes simplex virus (HSV-1, HSV-2) | Immune reaction, injury, deficiencies |
| Location | On or around lips, outside mouth | Inside mouth (tongue, cheeks, palate) |
| Appearance | Fluid-filled blisters, often in groups | White/yellow ulcer with red border |
| Contagious | Yes | No |
| Healing Time | 7–14 days | 7–10 days (minor), longer for severe |
| Treatment | Antiviral medication, SPF, pain relief | Topical anesthetics, avoid triggers |
Conclusion
Being able to distinguish a cold sore from a canker sore ensures you take the right steps for relief and prevention. Cold sores are contagious blisters caused by HSV-1 and usually occur outside the mouth, while canker sores are non-contagious ulcers inside the mouth triggered by irritation, immune response, or deficiencies.
Cold sores respond best to early antiviral treatment and preventive measures like lip SPF and stress management. Canker sores typically heal on their own but may benefit from topical pain relief and avoiding trigger foods.
If you experience persistent sores, unusually large or painful lesions, or frequent recurrences, seek medical advice to rule out underlying health issues.
Knowing the difference helps protect your health, prevent spreading infection, and make healing faster and more comfortable.
Read also: How to Draw a Skull: Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
5 FAQs (People Also Ask)
- What is the difference between a cold sore and a canker sore?
Cold sores are viral, contagious lesions on or around the lips. Canker sores are non-contagious ulcers inside the mouth with different causes. - How long do cold sores and canker sores last?
Cold sores usually heal in 7–14 days. Canker sores typically heal in 7–10 days for minor types but may take longer if severe. - Are cold sores contagious but canker sores not?
Yes. Cold sores spread through direct contact; canker sores cannot be transmitted. - What triggers outbreaks of cold sores or canker sores?
Cold sores are triggered by HSV reactivation from stress, sunlight, illness, or hormones. Canker sores can be triggered by stress, mouth injury, certain foods, or deficiencies. - How can I relieve pain from these sores?
For cold sores, use antiviral creams or tablets and keep the area clean. For canker sores, use topical anesthetics, avoid irritating foods, and rinse with mild solutions.